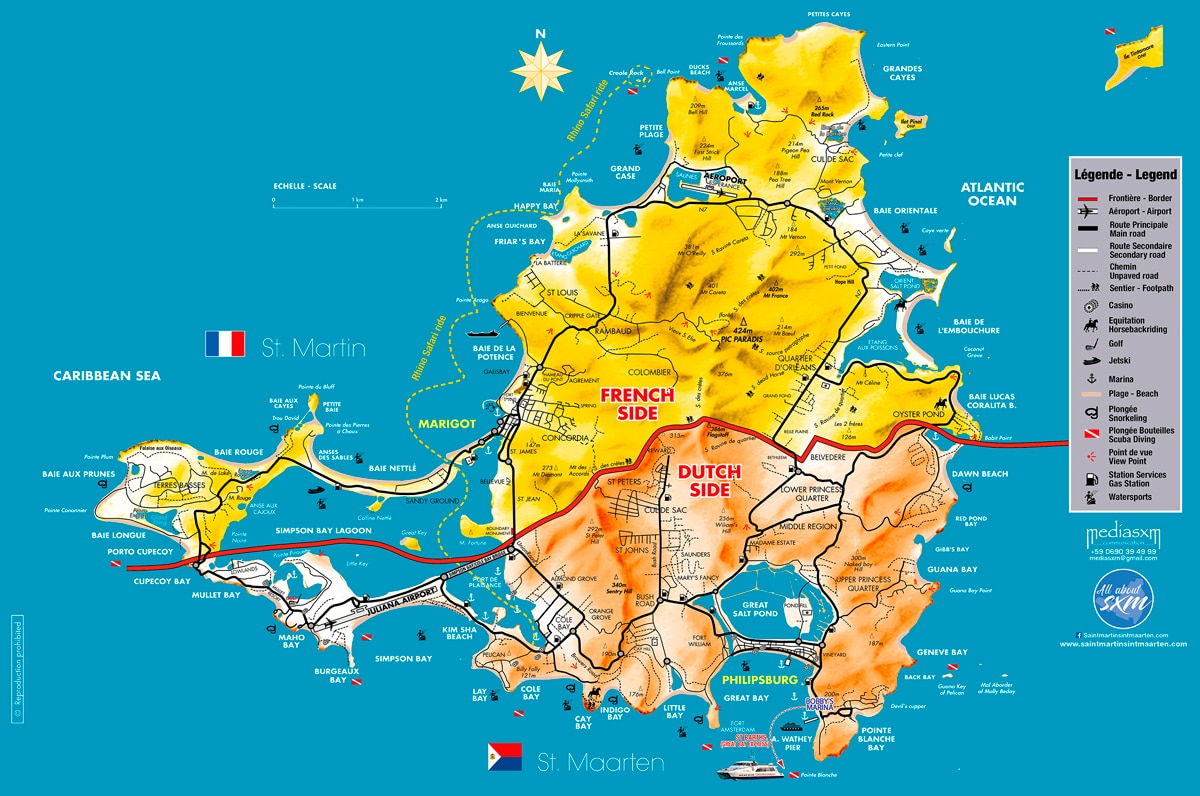
The island of St. Martin sits at the heart of the Antilles Archipelago in the Northern Hemisphere, between the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator.
More precisely, it lies towards the north of the Lesser Antilles, created when the Atlantic Plate slid under the Caribbean Plate to form the string of islands that includes Saint Martin.

Approximately 240km to the south east is the island of Guadeloupe. Saint Martin faces out towards the Atlantic on its eastern side and is washed by the waters of the Caribbean Sea on the west coast, an ideal geography.
With a total surface area of 88km², the island is 15km long and 13km wide at its longest and widest points.
The geography of Saint Martin occupies a central position midway between Puerto Rico and Guadeloupe at the heart of the Caribbean Sea, and is the closest part of France to US shores.

Saint Martin is a three-and-a-half-hour flight from New York, a two-and-a-half-hour flight from Miami (Florida), an hour and a half away from Caracas (Venezuela), and 45 minutes from the islands of Guadeloupe and Puerto Rico.
The island lies at around 7,000km and eight flight hours from Europe. Neighbouring islands include Anguilla, St Barts, Saba, Statia, Saint Kitts and Nevis. The highest hilltop is the Pic Paradis (424 metres (1,391 ft)) on center of a hill chain.
But both sides are hilly with large mountain peaks. This forms a valley were many houses are located.

There are no natural sources on the island of Sint Maarten. Many trails crisscross the forest allowing hikers to discover the geography of the island in a different aspect than the beaches.
Saint Martin’s Geography
Located in the northern part of the island, the French overseas community of Saint Martin has a total area of about 54 km2.
The inhabitants are known as Saint Martinois. Most of the built-up areas of the island are located in low-lying areas along the coast.
Since 2012, Saint Martin has gone from Town Hall to « Collectivité », which gives it the status of Overseas Territory. It is now directly dependent on France.
The capital is Marigot, home to the « Collectivité Hotel », the « Prefecture » and most of the « Collectivité Buildings » and administrative services. Grand Case, Colombier, Cul-de-Sac, Orleans Quarter, Nettlé Bay and Lowlands are other cities and districts.
There is no physical border between the French and Dutch geography and people and goods can travel freely between the two parts of the island.
The highest point of the island is Pic Paradis at 424 meters above the sea level.
Sint Maarten’s Geography
The Dutch part of the island, Sint Maarten, covers a total area of about 34 km2.
The inhabitants are known as Sint Maartiners. Most of the built-up areas of the island are located in low-lying areas along the coast, but are beginning to expand into mountainous areas.
Located in the southern part of the island, Sint Maarten was part of the Dutch West Indies, a group of five islands including Bonaire, Curacao, Saba, Statia and Sint Maarten. On October 10, 2010, Sint Maarten became a country in the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
The Dutch government remains responsible for defence and international policy within the framework of this autonomous status. This change of status put an end to the Dutch West Indies created in 1956.
The capital is Philipsburg, where Parliament and most of the buildings and administrative services are located. Other cities are Simpson Bay, Madame Estate, Cul de Sac, Dutch Quarter, Cole Bay, Oyster Pond, South Reward, St Peters, Pointe Blanche, Middle region, Cay Hill, Upper Prince’s Quarter and Lower Prince’s Quarter.